تم استخدام بيانات من Mars Express التابع لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية ESA و Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter التابع لناسا لإنشاء أول خريطة عالمية مفصلة للرواسب المعدنية المائية على المريخ. انظر أدناه للحصول على نسخة مشروحة مع أنواع المعادن ووفرتها. الائتمان: ESA / Mars Express (OMEGA) و NASA / Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (CRISM)
خريطة جديدة لـ[{” attribute=””>Mars is altering our perception of the planet’s watery past, and indicating potential landing sites for future missions.
The map shows mineral deposits across the red planet. It has been painstakingly created over the last decade using data from ESA’s Mars Express Observatoire pour la Mineralogie, l’Eau, les Glaces et l’Activité (OMEGA) instrument and NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) instrument.
Specifically, the map displays the locations and abundances of aqueous minerals. These come from rocks that have been chemically transformed by the action of water in the past, and have typically been converted into clays and salts.

Data from two Mars missions have been used to create the first detailed global map of hydrated mineral deposits on Mars. These minerals are predominately clays and salts, and can be used to tell the history of water in the planet’s various regions. For the most part, the clays were created on Mars during its early wet period, whereas many of the salts that are still visible today were produced as the water gradually dried up.
Various landing sites and areas of interest are shown on the map. Mawrth Vallis is an ancient water outflow channel that is rich in clays. Oxia Planum is another clay-rich region and has been selected as the landing site for ESA’s Rosalind Franklin rover. Meridiani Planum straddles the martian equator and was the landing spot for NASA’s Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity in 2004. Valles Marineris is one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. Gale crater and Jezero crater were the landing sites of NASA’s Curiosity and Perseverance rovers in 2012 and 2020 respectively.
The clays shown on the map include iron and magnesium phyllosilicates, zeolites, and aluminosilicate clays. The salts shown are carbonates made of carbon and oxygen. Credit: ESA/Mars Express (OMEGA) and NASA/Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (CRISM)
On Earth, clays are created when water interacts with rocks, with different conditions giving rise to different types of clays. For instance, clay minerals such as smectite and vermiculite form when relatively small amounts of water interact with the rock. Therefore, they retain mostly the same chemical elements as the original volcanic rocks. In the case of smectite and vermiculite, those elements are iron and magnesium. The rocks can be altered more when the amount of water is relatively high. Soluble elements tend to be carried away leaving behind aluminum-rich clays such as kaolin.
The big surprise for researchers is the prevalence of these minerals. Ten years ago, planetary scientists only knew of around 1000 outcrops on Mars. This made them interesting as geological oddities. However, the new map has reversed the situation, revealing hundreds of thousands of such areas in the oldest parts of the planet.
“This work has now established that when you are studying the ancient terrains in detail, not seeing these minerals is actually the oddity,” says John Carter, Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale (IAS) and Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille (LAM), Université Paris-Saclay and Aix Marseille Université, France.
https://www.youtube.com/watch؟v=JaYRi-6emYo
قامت Mars Express و Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter التابع لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية (ESA) برسم خرائط لصخور غنية بالمياه عبر المريخ. تعمل الخريطة العالمية الجديدة على تغيير طريقة تفكيرنا في الماضي المائي للكوكب ، وتوضح أين يمكننا أن نهب بعثات مستقبلية لمزيد من الاستكشاف. المفاجأة الكبيرة هي انتشار هذه المعادن ، حيث كشفت الخريطة عن مئات الآلاف من المواقع المتأثرة بالمياه في أقدم أجزاء الكوكب. ستساعد البيانات الجديدة في الإجابة عن أسئلة مثيرة حول تاريخ مناخ المريخ ، سواء كان الماء ثابتًا عالميًا أم محصورًا في فترات قصيرة ومكثفة ، وما إذا كانت الظروف مناسبة للحياة على الإطلاق. الائتمان: ESA – وكالة الفضاء الأوروبية
هذا نقلة نوعية في فهمنا لتاريخ الكوكب الأحمر. بدا من المعقول أن الماء كان محدودًا في مداه ومدته بناءً على عدد أقل من المعادن المائية التي عرفنا سابقًا وجودها. ومع ذلك ، لا يوجد شك الآن في أن الماء لعب دورًا كبيرًا في تشكيل الجيولوجيا في جميع أنحاء الكوكب.
الآن ، القضية الرئيسية المطروحة هي ما إذا كان الماء ثابتًا أم محصورًا في نوبات أقصر وأكثر شدة. على الرغم من عدم تقديم إجابة محددة بعد ، إلا أن النتائج الجديدة تمنح العلماء بالتأكيد أداة أقوى لمتابعة الإجابة.
يقول كارتر: “أعتقد أننا قمنا بشكل جماعي بتبسيط المريخ بشكل مفرط”. ويوضح أن علماء الكواكب يميلون إلى الاعتقاد بأن أنواعًا قليلة فقط من المعادن الطينية على المريخ تم تكوينها خلال فترة رطوبة المريخ ، ثم مع جفاف المياه تدريجيًا ، تم إنتاج الأملاح عبر الكوكب.
توضح هذه الخريطة الجديدة أنها أكثر تعقيدًا مما كان يعتقد سابقًا. في حين أن العديد من أملاح المريخ ربما تكونت في وقت متأخر عن الطين ، تظهر الخريطة العديد من الاستثناءات حيث يوجد خلط حميم من الأملاح والطين. حتى أن هناك بعض الأملاح التي يفترض أنها أقدم من بعض أنواع الطين.

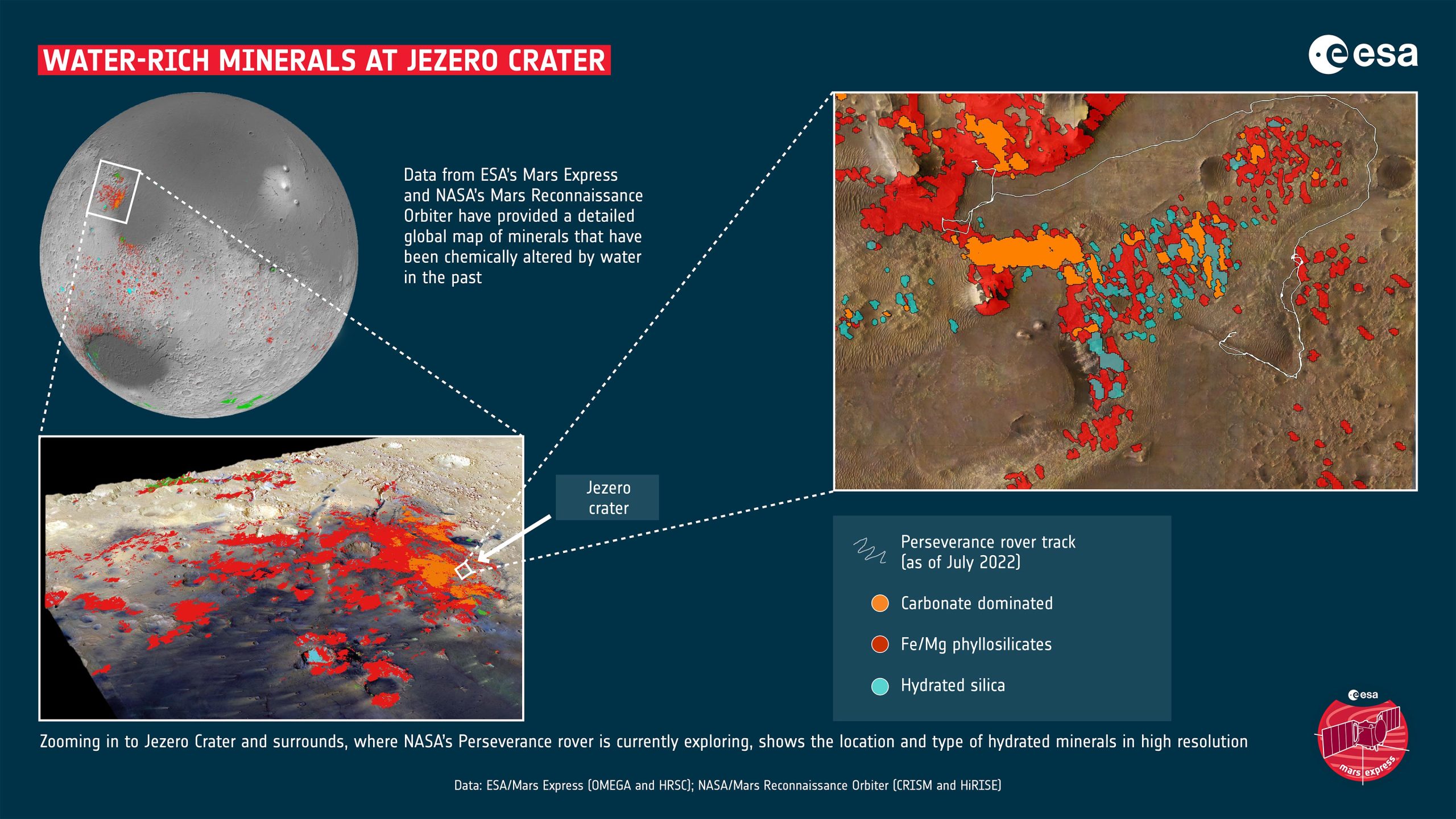
تعرض فوهة جيزيرو ومحيطها على سطح المريخ مجموعة غنية من المعادن التي تغيرت بفعل المياه في ماضي الكوكب. هذه المعادن هي في الغالب من الطين وأملاح الكربونات. من المعادن التي تم تحديدها في هذه المنطقة بالذات ، الكربونات عبارة عن ملح ، وسيليكات الحديد / المغنيسيوم عبارة عن طين غني بالحديد والمغنيسيوم ، والسيليكا المائية هي شكل من أشكال ثاني أكسيد السيليكون الذي يشكل أحجار العقيق الكريمة على الأرض. تم الحصول على بيانات عن قرب من خريطة عالمية للمعادن أنتجتها Mars Express التابع لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية ESA و Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter التابع لناسا. تستكشف مركبة المثابرة التابعة لوكالة ناسا ، والتي هبطت على سطح المريخ في عام 2020 ، حاليًا حفرة جيزيرو والمناطق المحيطة بها. الائتمان: ESA / Mars Express (OMEGA و HRSC) و NASA / Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (CRISM و HiRISE)
“التطور من الكثير من الماء إلى عدم وجود ماء ليس واضحًا كما كنا نعتقد ، لم يتوقف الماء بين عشية وضحاها. نرى تنوعًا كبيرًا في السياقات الجيولوجية ، بحيث لا يمكن لأي عملية أو جدول زمني بسيط تفسير تطور علم المعادن في المريخ. هذه هي النتيجة الأولى لدراستنا. والثاني هو أنه إذا استبعدت عمليات الحياة على الأرض ، فإن المريخ يعرض مجموعة متنوعة من المعادن في البيئات الجيولوجية تمامًا كما تفعل الأرض.
بعبارة أخرى ، كلما نظرنا عن كثب ، أصبح ماضي المريخ أكثر تعقيدًا.
تعتبر أدوات أوميغا وكريسم مناسبة بشكل مثالي لهذا المسح. مجموعات البيانات الخاصة بهم مكملة للغاية ، وتعمل على نفس نطاق الطول الموجي ، وحساسة لنفس المعادن. يوفر CRISM بشكل فريد تصويرًا طيفيًا عالي الدقة للسطح (حتى 15 مترًا / بكسل) لبقع كوكب المريخ شديدة التحديد ، ويجعله الأنسب لرسم خرائط للمناطق الصغيرة ذات الأهمية ، مثل مواقع هبوط المركبات الجوالة. على سبيل المثال ، يُظهر التعيين ذلك حفرة جيزيرو أين روفر 2020 الناسا يستكشف حاليًا ، ويعرض مجموعة متنوعة غنية من المعادن الرطبة.
من ناحية أخرى ، توفر أوميغا تغطية عالمية للمريخ بدقة طيفية أعلى ونسبة إشارة إلى ضوضاء أفضل. هذا يجعلها أكثر ملاءمة لرسم الخرائط العالمية والإقليمية ، والتمييز بين المعادن المتغيرة المختلفة.

كجزء من إنشاء خريطة عالمية جديدة لمعادن المريخ ، تم اكتشاف أن منطقة Oxia Planum غنية بالطين. تضمنت هذه الصلصال المعادن الغنية بالحديد والمغنيسيوم من السميكتايت والفيرميكوليت ، والكاولين محليًا ، والذي يُعرف على الأرض باسم الطين الصيني. يتم أيضًا تعيين السيليكا الرطبة فوق دلتا قديمة في أوكسيا. تم الحصول على بيانات عن قرب من خريطة عالمية للمعادن أنتجتها Mars Express التابع لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية ESA و Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter التابع لناسا. نظرًا لأن الطين يتكون في بيئات غنية بالمياه ، فإنه يجعل هذه المواقع مواقع ممتازة للدراسة بحثًا عن أدلة حول ما إذا كانت الحياة قد بدأت على المريخ. تم اختيار Oxia Planum كموقع هبوط لمركبة Rosalind Franklin الجوالة التابعة لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية. الائتمان: ESA / Mars Express (OMEGA و HRSC) و NASA / Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (CRISM)
تم عرض النتائج في ورقتين علميتين ، كتبهما كارتر ولوسي ريو وزملاؤه. كانت لوسي في معهد علوم الفضاء والملاحة الفضائية (ISAS) ، الوكالة اليابانية لاستكشاف الفضاء الجوي ([{” attribute=””>JAXA), Sagamihara, Japan, when part of the work was performed but is now an ESA Research Fellow at ESA’s European Space Astronomy Center (ESAC) in Madrid.
With the basic detections in hand, Lucie decided to take the next step and quantify the amounts of the minerals that were present. “If we know where, and in which percentage each mineral is present, it gives us a better idea of how those minerals could have been formed,” she says.
Due to two factors, this work also provides mission planners with several excellent candidates for potential future landing sites. First off, water molecules are still present in the aqueous minerals. Together with known locations of buried water-ice, this offers potential areas for water extraction for In-situ Resource Utilization, which is essential to the building of human bases on Mars. Salts and clays are often used construction materials on Earth.
Secondly, even before humans go to Mars, the aqueous minerals provide fantastic locations in which to perform science. As part of this mineral mapping campaign, the clay-rich site of Oxia Planum was discovered. These ancient clays include the iron and magnesium-rich minerals of smectite and vermiculite. Not only can they help unlock the planet’s past climate, but they are perfect sites to investigate whether there was once life on Mars. As such, Oxia Planum was proposed and finally selected as the landing site for ESA’s Rosalind Franklin rover.
“This is what I am interested in, and I think this kind of mapping work will help open up those studies going forward,” says Lucie.
As ever when dealing with Mars, the more we learn about the planet, the more fascinating it becomes.
References:
“A Mars Orbital Catalog of Aqueous Alteration Signatures (MOCAAS)” by John Carter, Lucie Riu, François Poulet, Jean-Pierre Bibring, Yves Langevin and Brigitte Gondet, 20 August 2022, Icarus.
DOI: 10.1016/j.icarus.2022.115164
“The M3 project: 3 – Global abundance distribution of hydrated silicates at Mars” by Lucie Riu, John Carter and François Poulet, 25 November 2021, Icarus.
DOI: 10.1016/j.icarus.2021.114809

“هواة الإنترنت المتواضعين بشكل يثير الغضب. مثيري الشغب فخور. عاشق الويب. رجل أعمال. محامي الموسيقى الحائز على جوائز.”